Granulomatous with polyangiitis (Wegener granulomatosis) is a multisystem autoimmune amenity of unfamiliar etiology which is rare.
What is the Pathology of is Granulomatous with Polyangiitis (Wegener Granulomatosis)?
The pathology of is granulomatous with polyangiitis (Wegener granulomatosis) is:
-Etiology: The cause of granulomatous with polyangiitis (Wegener granulomatosis) is a type of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody–allied vasculitis which largely targets small arteries.
-Genes involved: CTLA-4 (cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4).
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to granulomatous with polyangiitis (Wegener granulomatosis) may characterize some type of hypersensitivity.
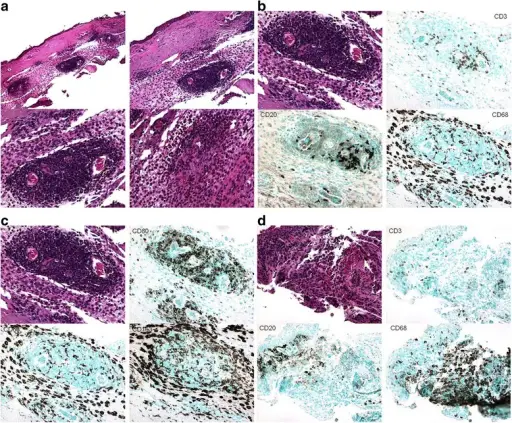
-Histology: The histology associated with granulomatous with polyangiitis (Wegener granulomatosis) shows granulomatous vasculitis or necrotizing of small and sometimes larger arteries.
How does Granulomatous with Polyangiitis (Wegener Granulomatosis) Present?
Patients with granulomatous with polyangiitis (Wegener granulomatosis) typically males are affected more often than females present at age range of about 40 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with granulomatous with polyangiitis (Wegener granulomatosis) include; mucosal ulcerations of the nasopharynx, persistent pneumonitis with bilateral nodular and cavitary infiltrates, chronic sinusitis, and evidence of renal disease.
How is Granulomatous with Polyangiitis (Wegener Granulomatosis) Diagnosed?
Granulomatous with polyangiitis (Wegener granulomatosis) is diagnosed through a Routine laboratory test: ESR. CBC, LFTs, Biopsy. P-ANCA testing. Imaging studies include sinus radiography and CT scan.
How is Granulomatous with Polyangiitis (Wegener Granulomatosis) Treated?
Granulomatous with polyangiitis (Wegener granulomatosis) is treated through medical care; mainstay medical treatment is an amalgamation of corticosteroids together with cytotoxic agents tailored to treat manifestations. Surgical care is considered in necrosis and damage to subglottic areas, bronchi trachea triggered by fibrosis.
What is the Prognosis of Granulomatous with Polyangiitis (Wegener Granulomatosis)?
The prognosis of granulomatous with polyangiitis (Wegener granulomatosis) is poor, linked with older age, board organ involvement, and board organ damage.