Hairy cell leukemia is a rare indolent lymphoproliferative neoplasm of mature B cells.
What is the Pathology of Hairy Cell Leukemia?
The pathology of hairy cell leukemia is:
-Etiology: The cause of hairy cell leukemia is associated with point mutations in the serine/threonine kinase BRAF.
-Genes involved: BRAF serine/threonine kinase gene.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to hairy cell leukemia is associated with activating point mutations in the serine/threonine kinase BRAF which lies immediately downstream of RAS in the MPAK signaling cascade.
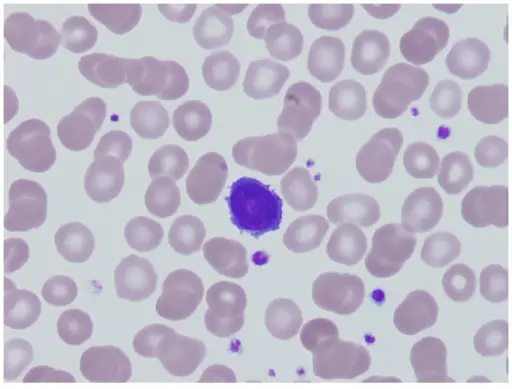
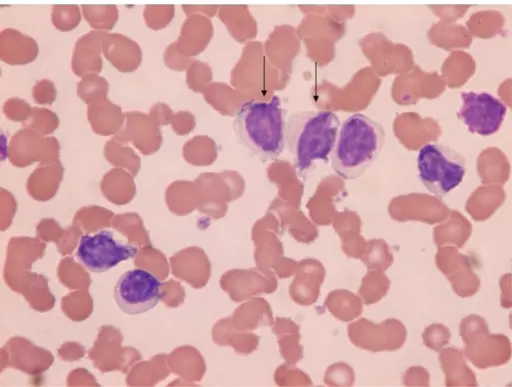
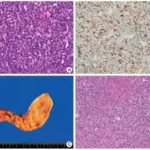
-Histology: The histology associated with hairy cell leukemia shows round, oblong or reniform nuclei and moderate amounts of pale blue cytoplasm with thread-like or bleb-like extensions. The number of circulating cells is highly variable. The marrow is involved by a diffuse interstitial infiltrate of cells with oblong or reniform nuclei, condensed chromatin and pale cytoplasm. In phase contrast microscopy, it shows tumor cells with fine hair-like cytoplasmic projections.
How does Hairy Cell Leukemia Present?
Patients with hairy cell leukemia are typically middle-aged white males with a median age of 55 and a male to female ratio of 5:1. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with hairy cell leukemia include largely from infiltration of the bone marrow, liver and spleen. Massive splenomegaly is the most common and sometimes the only abnormal physical finding. Pancytopenia may be present and there is an increased incidence of atypical mycobacterial infections.
How is Hairy Cell Leukemia Diagnosed?
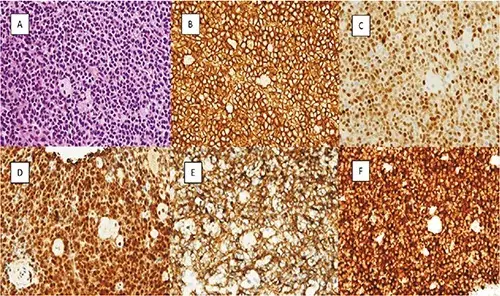
Hairy cell leukemia is diagnosed mainly through peripheral blood and bone marrow morphology, flow cytometry, immunophenotyping, immunohistochemistry, and molecular studies.
How is Hairy Cell Leukemia Treated?
Hairy cell leukemia is treated with chemotherapeutic regimens which produce long lasting remissions. BRAF inhibitors may appear to produce excellent responses in tumors that have failed conventional chemotherapy.
What is the Prognosis of Hairy Cell Leukemia?
The prognosis of hairy cell leukemia is excellent due to its chronic relatively indolent course that responds well to current chemotherapy. The 5 year event free survival rate after treatment is approximately 90%.