Hairy leukoplakia is a condition triggered by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). It causes white patches on your tongue.
What is the Pathology of Hairy Leukoplakia?
The pathology of hairy leukoplakia is:
-Etiology: The cause of hairy leukoplakia is the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV).
-Genes involved: EBNA-2 gene.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to hairy leukoplakia is clearly complex, potentially requiring a convergence of factors including EBV co-infection, productive EBV replication, EBV genetic evolution, expression of specific EBV “latent” genes, and immune escape.
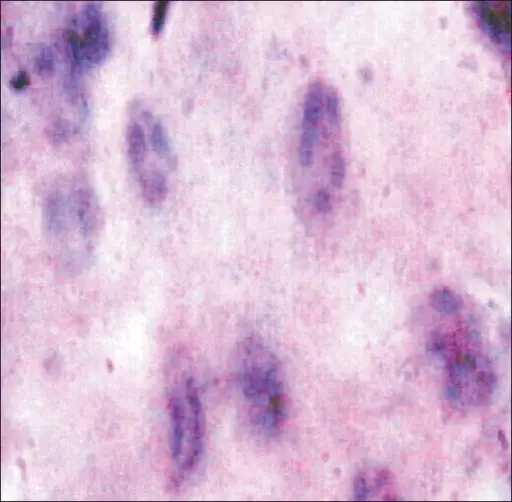
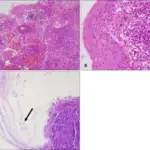
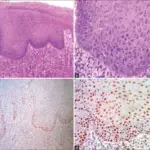
-Histology: The histology associated with hairy leukoplakia shows hyperkeratotic oral mucosa due to the piling of keratotic squamous epithelium.
How does Hairy Leukoplakia Present?
Patients with hairy leukoplakia typically affect males present in the range of 25 and above. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with hairy leukoplakia include white patch, which almost exclusively occurs on the lateral surfaces of the tongue, although rarely it may occur on the buccal mucosa, soft palate, pharynx, or esophagus. The lesion may grow to involve the dorsal surface of the tongue. The texture is vertically corrugated (“hairy”) or thickly furrowed and shaggy in appearance.
How is Hairy Leukoplakia Diagnosed?
Hairy Leukoplakia is diagnosed through biopsy.
How is Hairy Leukoplakia Treated?
Hairy Leukoplakia is treated by topical use of podophyllum resin or retinoids has also been reported to produce a temporary remission. Antiretroviral drugs such as zidovudine may be effective in producing a significant regression of OHL.
What is the Prognosis of Hairy Leukoplakia?
The prognosis of hairy leukoplakia is fair.