Heart failure or congestive heart failure is an abnormality in the normal function of the heart, where the heart is not able to pump an adequate amount of blood to supply the tissues.
What is the Pathology of Heart Failure?
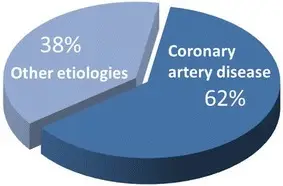
The pathology of heart failure is due to an injury in the myocardium caused by ischemia, hypertension, and diabetes.
How does Heart Failure Present?
Heart failure presents as exertional dyspnea, orthopnea, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, dyspnea at rest, and acute pulmonary edema.
How is Heart Failure Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of heart failure includes a thorough history and physical exam, 2D echo, chest x-ray, and echocardiogram. Blood work is also required such as serum urea and electrolytes, creatinine, full blood count, and liver and thyroid function tests.
How is Heart Failure Treated?
Treatment of heart failure includes diuretics, inotropes, ACE-I, beta blockers, SGLT2 inhibitors, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, right heart catheterization, dapagliflozin and/ or heart transplantation for advanced cases.
What is the Prognosis of Heart Failure?
Heart failure prognosis is poor, with mortality at 10% 30 days after admission, and at 42% 5-years after diagnosis.