Helicobacter pylori gastritis is bacteria that can cause an infection in the stomach or duodenum first part of the small intestine. It’s the most common cause of peptic ulcer disease. H. pylori can also inflame and irritate the stomach lining gastritis.
What is the Pathology of Helicobacter Pylori Gastritis?
The pathology of helicobacter pylori gastritis is:
-Etiology: The cause of helicobacter pylori gastritis is: bacteria that infect and inflame the stomach lining. The term gastritis refers specifically to abnormal inflammation in the stomach lining.
-Genes involved: Unknown.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to helicobacter pylori gastritisare infection in humans can be described in three steps: entry to adherence to and colonization of the human gastric mucosa, exploitation of the human immune system and transmission to a new susceptible host.
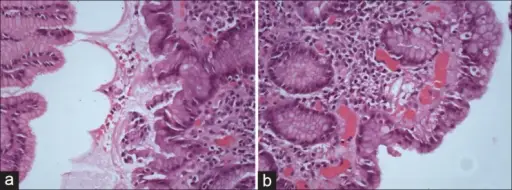
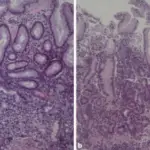
-Histology: The histology associated with pylori gastritis are: irregular surface epithelium, loss of apical mucin, cell dropout, formation of pits and microerosions.
How does Helicobacter Pylori Gastritis Present?
Patients with helicobacter pylori gastritis typically more in males present under age of 5 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with helicobacter pylori gastritis include: dull or burning pain in your stomach more often a few hours after eating and at night, unplanned weight loss, bloating, nausea and vomiting bloody vomit, indigestion dyspepsia, burping, loss of appetite.
How is Helicobacter Pylori Gastritis Diagnosed?
Helicobacter pylori gastritis is diagnosed by urea breath test, stool antigen test, and testing of endoscopic biopsy samples.
How is Helicobacter Pylori Gastritis Treated?
Helicobacter pylori gastritis is treated by antibiotics, and a proton pump inhibitor.
What is the Prognosis of Helicobacter Pylori Gastritis?
The prognosis of helicobacter pylori gastritis is fair. H. pylori infection is not easily cured, and research has shown that multidrug therapy is required. As with any bacterial infection, therapy must include antimicrobial agents to which the bacterium is sensitive.