Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia is the development of thrombocytopenia, due to the administration of various forms of heparin.
What is the Pathology of Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia?
The pathology of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia is:
-Etiology: The cause of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia is IgG antibodies that bind to platelet factor 4 on platelet membranes in a heparin-dependent fashion.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to heparin-induced thrombocytopenia shows that resultant activation of the platelets induces their aggregation, thereby exacerbating the condition that heparin is used to treat—thrombosis. Both venous and arterial thromboses occur, even in the setting of marked thrombocytopenia.
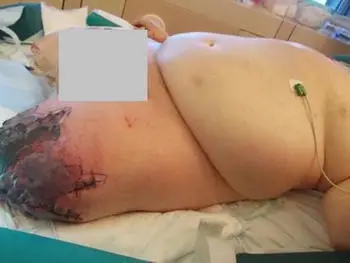
-Histology: The histology associated with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia shows skin lesions associated with the use of low-molecular-weight heparins.
How does Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia Present?
Patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia typically affect females present at the age range of over 50. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia include that affected patients usually have a reduction in platelet count within 4 – 20 days after heparin exposure for the first time, 1 – 3 days after reexposure to heparin; platelet count typically decreases 50% or more to under 100K. The symptoms include enlargement or extension of a previously diagnosed blood clot, or the development of a new blood clot elsewhere in the body, skin tenderness, swelling, skin that’s warm to the touch, shortness of breath, change in heart rate, sharp pain in chest, dizziness, and anxiety.
How is Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia Diagnosed?
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia is diagnosed using ELISA methodology and 4 T score.
How is Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia Treated?
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia is treated by the cessation of heparin and by using low-molecular-weight heparin preparations.
What is the Prognosis of Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia?
The prognosis of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia is poor and can cause severe morbidities such as loss of limb or death.