Hepatoblastoma is a rare type of childhood cancer that occurs in the liver
What is the Pathology of Hepatoblastoma?
The pathology of hepatoblastoma is:
-Etiology: The cause of hepatoblastoma is sporadic
-Genes involved: (if any just mention the genes here)
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to hepatoblastoma arises from primary hepatoblasts or multipotent hepatic progenitor cells
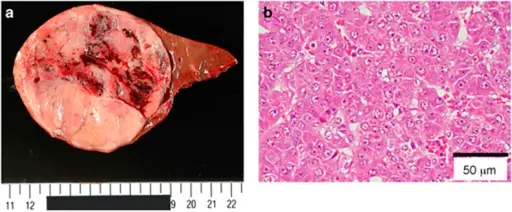
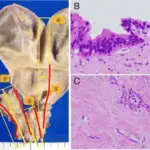
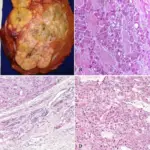
-Histology: The histology associated with hepatoblastoma shows solid nests or glandular/acinar morphology, with papillae and pseudorosettes
How does Hepatoblastoma Present?
Patients with hepatoblastoma typically affect children( male) present at the age range of 5 months to 6 years old. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with hepatoblastoma include abdominal enlargement, mass or pain, jaundice, anorexia, and weight loss.
How is Hepatoblastoma Diagnosed?
Hepatoblastoma is diagnosed using fine needle aspiration and biopsy.
How is Hepatoblastoma Treated?
Hepatoblastoma is treated with chemotherapy and surgical intervention. Liver transplantation may needed in some cases.
What is the Prognosis of Hepatoblastoma?
The prognosis of hepatoblastoma is good with the survival rate be around 90%.