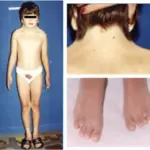
Hermaphroditism is an intersex condition in which an individual is born with both ovarian and testicular tissue.
What is the Pathology of Hermaphroditism?
The pathology of Hermaphroditism is:
-Etiology: The causes of Hermaphroditism are different types of gonads.
-Genes involved: SRY gene.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to Hermaphroditism coexistence of seminiferous tubules and ovarian follicles.
How does Hermaphroditism Present?
Patients with hermaphroditism typically present at birth. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with (disease in lower case) include ambiguous genitalia.
How is Hermaphroditism Diagnosed?
Hermaphroditism is diagnosed by initial investigations include chromosome analysis and an ultrasound scan to check the internal reproductive organs. Patients who present later in life have higher differentiation of genitalia. Diagnosis requires careful anatomical assessment via imaging modalities and/or laparoscopy. Biochemical endocrine investigation, cytogenetic and molecular genetic tests are also useful.
How is Hermaphroditism Treated?
Hermaphroditism is treated with hormone replacement and psychological support.
What is the Prognosis of Hermaphroditism?
The prognosis of hermaphroditism is good. Patients usually have normal life expectancy.