Herpes simplex virus is an infection that appears in various parts of the body, most commonly on the genitals or mouth.
What is the Pathology of Herpes Simplex Virus?
The pathology of herpes simplex virus is:
-Etiology: The cause of herpes simplex virus is direct contact, sexual contact.
-Genes involved: Not applicable.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to herpes simplex virus shows that during lytic replication HSV produces infectious viral particles to infect other cells and organisms, while during latency there is limited gene expression and lack of infectious virus particles.
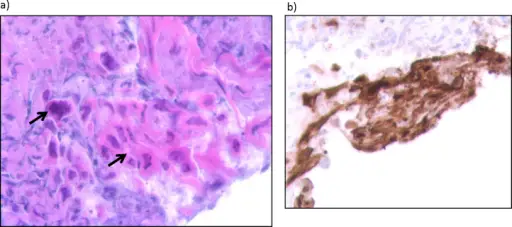
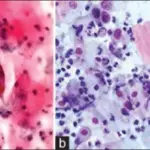
-Morphology: The morphology associated with herpes simplex virus shows open scalloped sores, or sores in the process of healing.
-Histology: The histology associated with herpes simplex virus shows multinucleated giant cells with ground glass nuclei.
How does Herpes Simplex Virus Present?
Patients with herpes simplex virus typically are all genders at age range of 14 – 49years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with herpes simplex virus include fever, pain with urination, tingling sensations, and skin sores.
How is Herpes Simplex Virus Diagnosed?
Herpes simplex virus is diagnosed by blood test.
How is Herpes Simplex Virus Treated?
Herpes simplex virus is treated by antiviral medications such as acyclovir, famciclovir, and valacyclovir.
What is the Prognosis of Herpes Simplex Virus?
The prognosis of herpes simplex virus is fair.