Histoplasma fungal infection is an infection caused by breathing in spores of a fungus often found in bird and bat droppings.
What is the Pathology of Histoplasma Fungal Infection?
The pathology of histoplasma fungal infection is:
-Etiology: The cause of histoplasma fungal infection is breathing in spores of a fungus often found in bird and bat droppings.
-Genes involved: Not applicable.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to histoplasma fungal infection are:
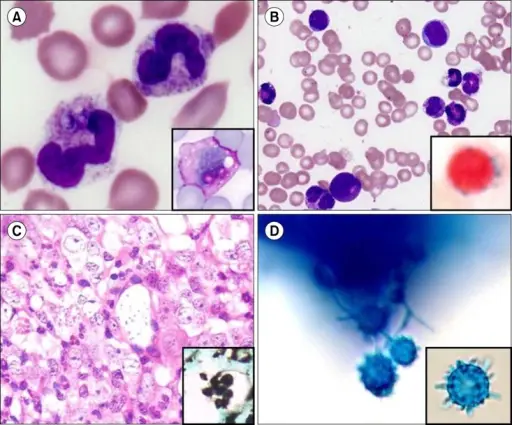
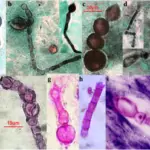
-Morphology: The morphology associated with histoplasma fungal infection shows delicate, septate hyphae, 1 – 2 microns thick, with large rough walled macroconidia 5 – 15 microns.
-Histology: The histology associated with histoplasma fungal infection shows isolated intracellular organisms and large aggregates surrounded by chronic inflammatory cells and fibroblasts.
How does Histoplasma Fungal Infection Present?
Patients with histoplasma fungal infection typically are all genders of all ages. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with histoplasma fungal infection include chest pain, body aches, fever, chils, and headaches.
How is Histoplasma Fungal Infection Diagnosed?
Histoplasma fungal infection is diagnosed by blood test or a urine test.
How is Histoplasma Fungal Infection Treated?
Histoplasma fungal infection is treated by antibiotics such as Itraconazole.
What is the Prognosis of Histoplasma Fungal Infection?
The prognosis of histoplasma fungal infection is fair to poor. If untreated, subacute progressive disseminated histoplasmosis results in death within 2-24 months.