Hunington’s disease is neurodegenerative disorder of the central nervous system characterized by unwanted choreatic movements, behavioral and psychiatric disturbances and dementia.
What is the Pathology of Huntington’s Disease?
The pathology of Hunington’s disease is:
-Etiology: The cause of Huntington’s disease is autosomal dominant trinucleotide (CAG)repeat expansion in the huntingtin (HTT) gene on chromosome 4.
-Genes involved: Huntingtin (HTT) gene on chromosome 4.
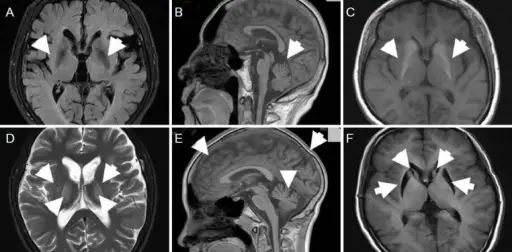
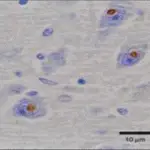
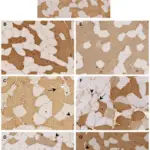
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to Huntington’s disease is expansion of CAG repeats of cytosine-adenine-guanine in the gene coding for the Huntington protein. Damage may occur in the subcortical basal ganglia, initially in the striatum, but as the disease progresses, other areas of the brain are also affected, including regions of the cerebral cortex. Early symptoms include abnormal movements, and mood changes.
How does Huntington’s Disease Present?
Patients with Huntington’s disease typically are males over forty years old. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with Huntington’s disease include chorea, athetosis, aggression, depression, dementia.
How is Huntington’s Disease Diagnosed?
Huntington’s disease is diagnosed basing on physical exam. Genetic testing can be used to confirm a physical diagnosis if no family history of HD exists. Even before the onset of symptoms, genetic testing can confirm if an individual or embryo carries an expanded copy of the trinucleotide repeat (CAG) in the HTT gene that causes the disease. Genetic counseling is available to provide advice and guidance throughout the testing procedure and on the implications of a confirmed diagnosis.
How is Huntington’s Disease Treated?
Huntington’s disease treatment involves management of symptoms which include dopamine blockers. Anxiolytic and antidepressant therapy may be necessary.
What is the Prognosis of Huntington’s Disease?
The prognosis of Huntington’s disease is fair. Life expectancy is around 20 years following the onset of visible symptoms.