Hyperthyroidism is a syndrome allied to excess thyroid hormone production and secretions.
What is the Pathology of Hyperthyroidism?
The pathology of hyperthyroidism is:
-Etiology: The cause of hyperthyroidism is an autoimmune disease Graves’ disease, multinodular goiter, and thyroxine-secreting tissue.
-Genes involved: TSH receptor gene (TSHR).
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to hyperthyroidism, underlying autoimmune cause, there is the production of thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulins which bind to the TSH receptor, mimic the TSH effects. Autonomous ectopic tissue in multinodular goiter causes excess production of thyroid hormone, causing clinical thyrotoxicosis.
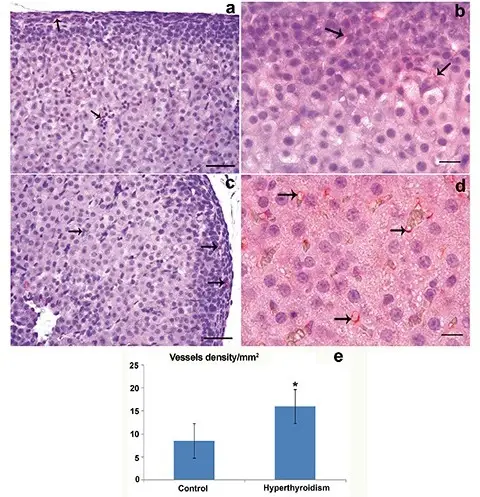
-Morphology: The morphology associated with hyperthyroidism shows diffuse and toxic nodular hyperplasia.
-Histology: The histology associated with hyperthyroidism shows lymphocytic penetration, diffuse follicular and papillary hyperplasia.
How does Hyperthyroidism Present?
Patients with hyperthyroidism typically more in females (2.7%) than males (0.23%) present at age range 20-40 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with hyperthyroidism include anxiety, hyperactivity, increased perspiration, Nervousness, Palpitations, muscle weakness heat intolerance tachycardia, hand tremor.
How is Hyperthyroidism Diagnosed?
Hyperthyroidism is diagnosed through history and physical examination. Laboratory studies for thyroid function test indicates reduced TSH and increased T3 and T4, anti-thyroid peroxidase (anti-TPO) antibody test, autoantibody titers, scintigraphy, and radioisotope thyroid scan may be useful.
How is Hyperthyroidism Treated?
Hyperthyroidism is treated through symptoms relief, thionamide therapy, iodine radioactive therapy, and subtotal thyroidectomy.
What is the Prognosis of Hyperthyroidism?
The prognosis of hyperthyroidism is good disease is associated with definitive positive treatment.