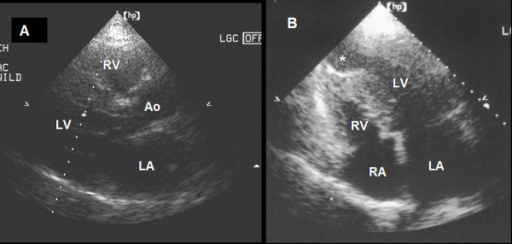
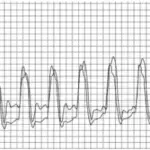
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a genetic disease characterized by an increase in the left ventricular wall thickness.
What is the Pathology of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy?
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy pathology is due to mutation of cardiac sarcomere protein genes transmitted in an autosomal dominant trait.
How does Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Present?
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy presents as dyspnea, syncope, presyncope, angina, palpitations, orthopnea, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, congestive heart failure, dizziness, and sudden cardiac death.
How is Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Diagnosed?
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy diagnosis include 2D echo, routine laboratory tests and genetic testing.
How is Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Treated?
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy treatment includes beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, and antitussives. Surgery, alcohol ablation or pacing is also conducted.
What is the Prognosis of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy?
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy prognosis is good with an annual mortality of only <1%-6%.