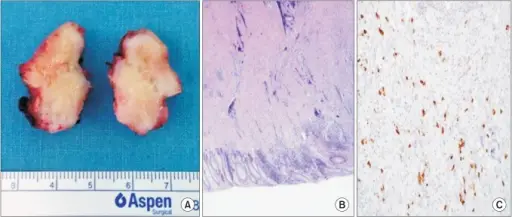
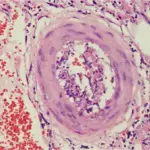
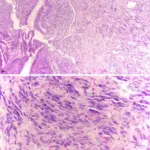
IgG4-related disease is a new rare syndrome that is associated with many disease processes.
What is the Pathology of IgG4-Related Disease?
The pathology of IgG4-related disease is:
-Etiology: The cause of IgG4-related disease is unknown, but may be attributed to an autoimmune and allergic disorder.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to IgG4-related disease starts with autoantigens that trigger the condition, with IgG4 antibodies proven to be not pathogenic themselves and are released due to immunologic response to infection.
-Morphologic changes: The morphologic changes involved with IgG4-related disease are inflammatory pseudotumors, lymphoplasmacytic infiltration, and storiform fibrosis.
How does IgG4-Related Disease Present?
IgG4-related disease typically affects male in the head and neck region and present at age range of 50-55 years old. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with IgG4-related disease include swelling of involved organ, pancreatitis, lymphadenopathy, hypothyroidism, bile duct lesion, salivary and lacrimal gland involvement, allergies and plaques, papules and nodules that are pruritic and most commonly located in the face or forearm.
How is IgG4-Related Disease Diagnosed?
IgG4-related disease is diagnosed through the combination of clincial, radiology, serologic, and endoscopic examination. Definite diagnosis requires biopsy.
How is IgG4-Related Disease Treated?
IgG4-related disease is treated with systemic steroids, azathioprine, mycophenolate mofetil, and rituximab.
What is the Prognosis of IgG4-Related Disease?
The prognosis of IgG4-related disease is dependent on its manifestation, that can either result to spontaneous resolution or progress to persistent and relapsing symptoms.