Immune complex-associated vasculitis is a disease that occurs as a result of the accumulation of the immune complexes in the blood vessels causing them to become inflamed it’s mostly seen in immunological disorders.
What is the Pathology of Immune Complex- Associated Vasculitis?
The pathology of immune complex-associated vasculitis is:
-Etiology: The cause of immune complex-associated vasculitis may be due to an infection, medication, autoimmune disorders,
-Genes involved: Unknown.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to immune complex-associated vasculitis accumulates the immunoglobulins in the blood vessels.
-Morphology: NA.
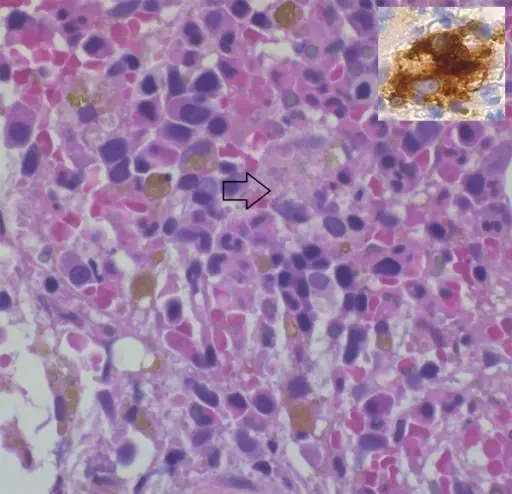
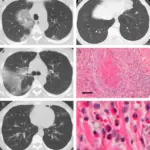
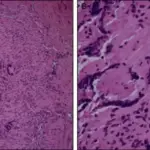
-Histology: The histology associated with immune complex-associated vasculitis is the presence of infiltrating leucocytes and fibrinoid necrosis.
How does Immune Complex-Associated Vasculitis Present?
Patients with immune complex-associated vasculitis typically are males. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with immune complex-associated vasculitis include palpable purpura which are cutaneous palpable lesions in the lower extremities,
How is Immune Complex-Associated Vasculitis Diagnosed?
Immune complex-associated vasculitis is diagnosed with x-rays, CT-scan, ultrasounds, and MRI.
How is Immune Complex-Associated Vasculitis Treated?
Immune complex-associated vasculitis is treated through corticosteroids and immunosuppressors.
What is the Prognosis of Immune Complex-Associated Vasculitis?
The prognosis of immune complex-associated vasculitis is good since it has a low mortality rate and one can recover in months.