Immunologic tolerance is a complex set of mechanisms keeps that impairs the immune system’s ability to properly have an immune responses against self-antigens. It is a state of inactivity in which lymphocytes remain alive but unable to perform physiological functions.
What is Immunologic Tolerance?
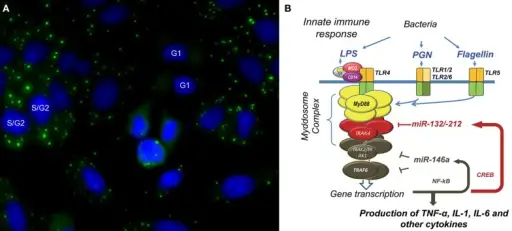
Glycine (G)–Tryptophan (W) bodies (GWBs) and microRNA regulation in the innate immune response. (A) Using a human prototype serum, we identified a novel cytoplasmic domain (green) in HEp-2 anti-nuclear antibody assay; nuclei are counterstained blue with DAPI. (B) Our proposed model of microbial tolerance and cross-tolerance is regulated by miRNAs via targeting of the Myddosome complex. Our Journey from the Study of Human Autoantibodies to the microRNA World: Fredenburg KM, Chan EK - Frontiers in immunology (2015). Not altered. CC.