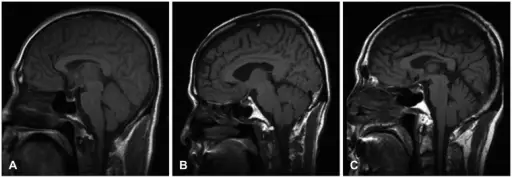
Infection related adrenocortical insufficiency is the clinical manifestation of absence or deficiency in the production of glucocorticoids due to infection.
What is the Pathology of Infection Related Adrenocortical Insufficiency?
The pathology of infection related adrenocortical insufficiency is:
-Etiology: The cause of infection related adrenocortical insufficiency are tumors, tuberculosis and other types of infections, and auto-immunity.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to infection related to adrenocortical insufficiency is that it occurs most often when patients have an autoimmune disease that causes the body to attack the glands.
How does Infection Related Adrenocortical Insufficiency Present?
Patients with infection related adrenocortical insufficiency typically are either male or female present at the age range of all age groups. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with infection related adrenocortical insufficiency include anorexia, orthostatic hypotension, salt craving, weakness, fatigue, and hyperpigmentation of the skin.
How is Infection Related Adrenocortical Insufficiency Diagnosed?
Infection related adrenocortical insufficiency is diagnosed with difficulties because many of these symptoms are mild at first and may go unnoticed.
How is Infection Related Adrenocortical Insufficiency Treated?
Infection related adrenocortical insufficiency is treated with hormone replacement therapy to replace cortisol.
What is the Prognosis of Infection Related Adrenocortical Insufficiency?
The prognosis of infection related adrenocortical insufficiency is good if properly treated.