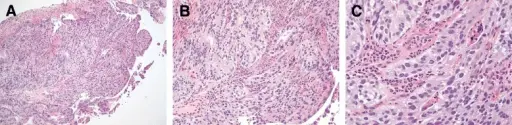
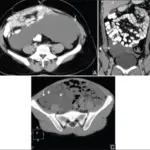
Inferior vena cava syndrome is the condition caused by compression or invasion of the inferior vena cava wall and/or thrombus from iliac or femoral vein.
What is the Pathology of Inferior Vena Cava Syndrome?
The pathology of inferior vena cava syndrome is:
-Etiology: The cause of inferior vena cava syndrome is neoplasms, thrombus
-Genes involved: Unknown.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to inferior vena cava syndrome are as the result of consequent obstruction of inferior vena cava by neoplastic invasion and a thrombus producing the clinical manifestation.
-Morphology: Unknown.
-Histology: Unknown.
How does Inferior Vena Cava Syndrome Present?
Patients with inferior vena cava syndrome are typically more common in males within an age range of 40 to 60 years old. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with inferior vena cava syndrome include edema of the leg, abdominal superficial collateral veins distension.
How is Inferior Vena Cava Syndrome Diagnosed?
Inferior vena cava syndrome is diagnosed through imaging studies such as chest radiography, CT scan, MRI, and venography.
How is Inferior Vena Cava Syndrome Treated?
Inferior vena cava syndrome is treated through medical care which may include chemotherapy and oxygen supplementation. Surgical care like a surgical bypass may be helpful.
What is the Prognosis of Inferior Vena Cava Syndrome?
The prognosis of inferior vena cava syndrome is good. With proper management, it is not associated with any mortality.