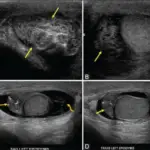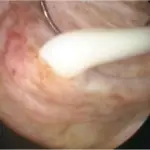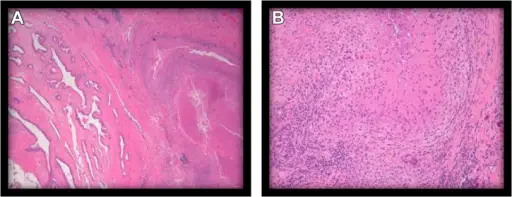
Pathologic slides of the prostate: normal prostatic tissue (left) adjacent to necrotizing granulomatous tissue (A) and lymphocytic reaction representing acute or chronic inflammation (B). Nonspecific Presentation of a Multiloculated Prostatic Abscess After Transurethral Prostatic Biopsy for Elevated Prostate-specific Antigen Level.
Gandhi NM, Lin J, Schaeffer E - Urology case reports (2014). Not Altered. CC.
Inflammation of the prostate is a clinical condition known as prostatitis characterized by pain, swelling, and appearance of red in color of the prostate secondary to an infection.
Examples of inflammation of the prostate includes:
- Acute bacterial prostatitis
- Chronic bacterial prostatitis
- Chronic a-bacterial prostatitis
- Granulomatous prostatitis