Intermediate metabolism involves molecules that are the precursors or metabolites of biologically significant molecules such as acetyl CoA.
What is Intermediate Metabolism?
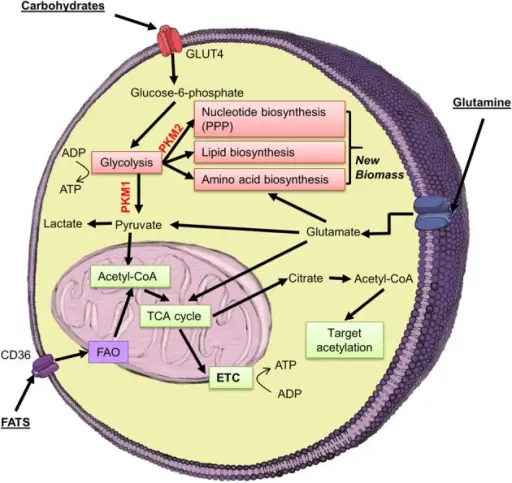
Intermediate Metabolism. Highly proliferative cell populations, such as some tumors, ESCs, iPSCs, and SCs require a ready supply of carbon and nitrogen for the generation of new biomass (nucleotides, proteins, phospholipids). To achieve this, many highly proliferative cell populations switch to a predominantly glycolytic based metabolism, but upregulate the PKM2 splice isoform of pyruvate kinase. In this manner, proliferating cells can build up sufficient glycolytic intermediates for the biomass necessary for cell division. A metabolic link to skeletal muscle wasting and regeneration. Koopman R, Ly CH, Ryall JG - Frontiers in physiology (2014). Not Altered. CC.