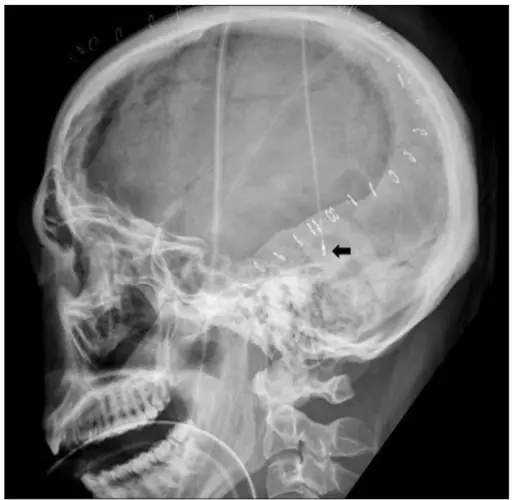
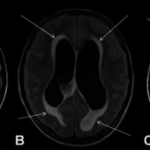
Intracranial pressure is the pressure exerted by fluids in the brain tissue inside the skull. This is mainly generated by cerebrospinal fluid. The normal value of CSF in a supine adult is 7-15 mmHg.
Raised intracranial pressure refers to the growing pressure inside the skull, above 20 mmHg. It leads to headache, vomiting, nausea, back pain, papilledema, ocular palsies and drowsiness.
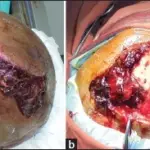
One major complication of increased intracranial pressure is brain herniation.