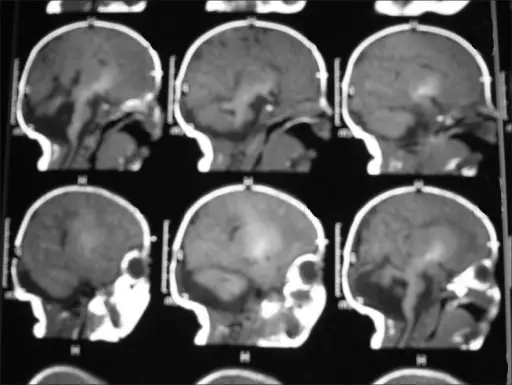
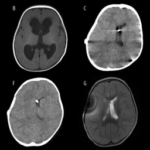
Joubert syndrome is a rare, autosomal recessive congenital cerebellar ataxia characterized by congenital malformation of the brainstem and agenesis or hypoplasia of the cerebellar vermis.
What is the Pathology of Joubert Syndrome?
Etiology: The cause of Joubert syndrome is an autosomal recessive genetic condition that causes problems with the structure and function of cilia.
Genes involved: OFD1, AHI1, NPHP1, and TMEM216
Pathogenesis: Genetic related improper formation of cilia.
How does Joubert Syndrome Present?
Patients with Joubert syndrome are typically males moreso than females. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with Joubert syndrome include nystagmus, abnormal breathing, ataxia, and developmental delay.
How is Joubert Syndrome Diagnosed?
Joubert syndrome is diagnosed by an MRI scan, which shows the absence or underdevelopment of the cerebellar vermis.
How is Joubert syndrome Treated?
Joubert syndrome is treated symptomatically.
What is the Prognosis of Joubert syndrome?
The prognosis of Joubert syndromes is poor with an average lifespan of 8 years old. Respiratory failure is the most common cause of death.