Kaposi sarcoma is a vascular neoplasm caused by Kaposi sarcoma herpesvirus (KSHV) (human herpesvirus-8, HHV-8)
What is the Pathology Kaposi Sarcoma?
The pathology of kaposi sarcoma is:
-Etiology: The cause of kaposi sarcoma is Kaposi sarcoma herpesvirus
-Genes involved: Unknown.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to kaposi sarcoma as the result of KSHV and altered T cell immunity. KSHV cause the lytic and latent infections at endothelial cells. Infected cells, KSHV-encoded proteins disturb usual cellular propagation controls by synthesis of cyclin D, viral homologue.
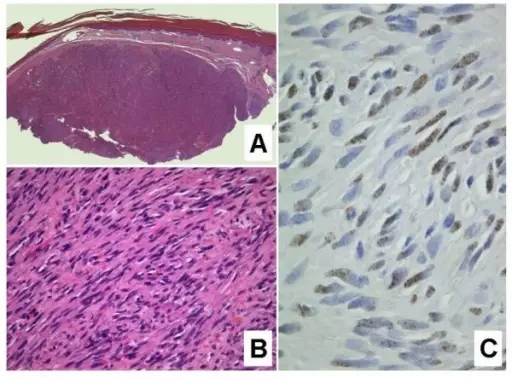
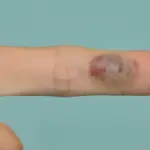
-Morphology: The morphology associated with kaposi sarcoma shows pink, red, or purple macules.
-Histology: The histology associated with kaposi sarcoma shows erupted erythrocytes, hemosiderin-laden macrophages, spindle cells proliferation.
How does Kaposi Sarcoma Present?
Patients with Kaposi sarcoma are typically males or females with HIV. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with kaposi sarcoma include among others, pink, red, or purple macules, raised plaques, hemoptysis, dyspnea.
How is Kaposi Sarcoma Diagnosed?
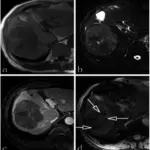
Kaposi sarcoma is diagnosed through laboratory studies to check for CD4 lymphocyte counts. Imaging studies such as radiography, bronchoscopy, esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD)/colonoscopy. Biopsy is diagnostic.
How is Kaposi Sarcoma Treated?
Kaposi sarcoma is treated through medical care which may include antiretroviral therapy, radiation therapy laser therapy, cryotherapy, topical retinoids. Surgical excision may be helpful.
What is the Prognosis of Kaposi Sarcoma?
The prognosis of Kaposi sarcoma is poor.