Kawasaki disease is also known as mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome. Kawasaki disease is an acute illness characterized by inflammation of blood vessels in the whole body.
What is the Pathology of Kawasaki Disease?
The pathology of Kawasaki disease is:
-Etiology: The cause of Kawasaki disease is unknown but the possible causes considered are infectious, genetic, toxic, and immunological factors.
-Genes involved: Unknown.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to Kawasaki disease is not known but there is the involvement of the immunopathologic mechanism after the inflammatory process has occurred
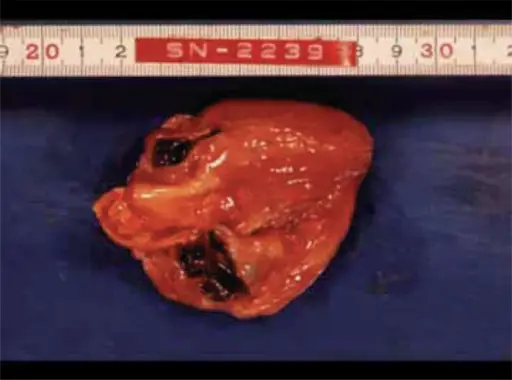
-Morphology: The morphology associated with Kawasaki disease shows a dense accumulation of macrophages and
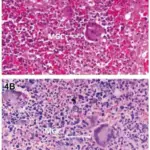
-Histology: The histology associated with Kawasaki disease shows lymphocytes and mononuclear cells, pustules with small intraepidermal, edema of the papillary dermis, and subcorneal abscesses.
How does Kawasaki Disease Present?
Patients with Kawasaki disease typically are pediatric males. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with Kawasaki disease include abnormal appearing tounge, skin rashes, rhinorrhea, vomiting, diarrhea, arthritis, arthralgia, and irritability.
How is Kawasaki Disease Diagnosed?
Kawasaki disease is diagnosed using electrocardiograph, chest x-ray, and physical examination.
How is Kawasaki Disease Treated?
Kawasaki disease is treated by Asprin and the dosage depends on the stage of the disease.
What is the Prognosis of Kawasaki Disease?
The prognosis of Kawasaki disease is fair since the treated child can recover in ten days.