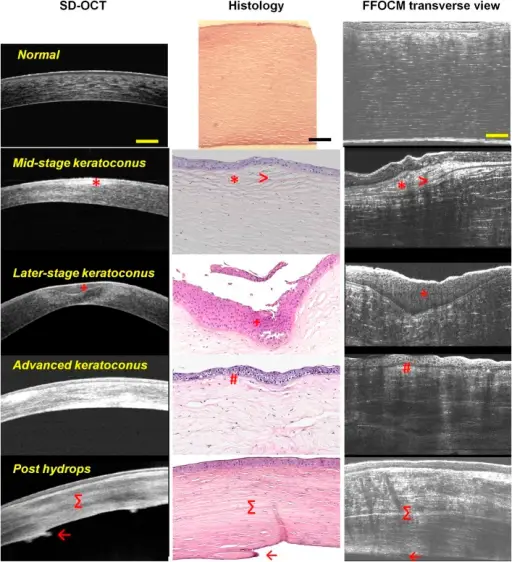
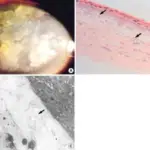
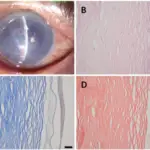
Keratoconus is an uncommon corneal disorder whereby there is thinning and steepening of the central cornea or paracentral cornea.
What is the Pathology of Keratoconus?
The pathology of Keratoconus is corneal scarring, fragment of bowman’s layer, thinning of overlying epithelial and stroma.
How does Keratoconcus Present?
Keratoconcus presents with Munson’s sign, asymmetric refractive error, progressive astigmatism, breaks in bowman’s membrane.
How is Keratoconus Diagnosed?
Keratoconus is diagnosed by slit lamp examination, video keratography, ultrasound pachymetry, physical examination.
How is Keratoconus Treated?
Keratoconus is treated with soft toric contact lenses, corneal collagen cross-linking, cycloplegic agent, and surgery.
What is the Prognosis of Keratoconus?
The prognosis of Keratoconus is with proper treatment, patients retain normal vision but in most cases with lenses.