Laryngitis is inflammation of the larynx.
What is the Pathology of Laryngitis?
The pathology of laryngitis is:
-Etiology: The cause of laryngitis include exposure to noxious agents, vocal misuse, and/ or infectious agents causing upper respiratory tract infections
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to laryngitis is inflamation.
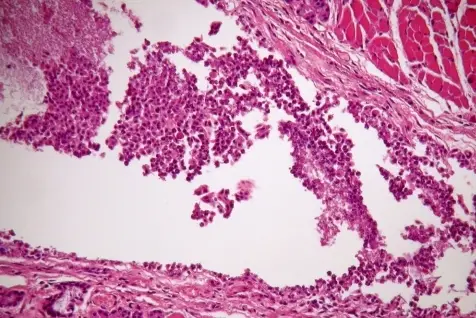
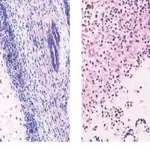
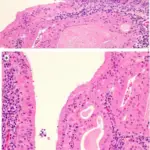
-Histology: The histology associated with laryngitis shows The study of inflammation to the larynx and the vocal fold mucosa.
How does Laryngitis Present?
Patients with laryngitis typically affect both genders though the prevalence is not documented, present at age range of 18-40 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with laryngitis include; dysphonia, cough, rhinitis, fever, postnasal discharge, malaise, congestion, fatigue, and sore throat.
How is Laryngitis Diagnosed?
Laryngitis is diagnosed thorough medical history and physical examination. Imaging, indirect laryngoscopy.
How is Laryngitis Treated?
Laryngitis is treated through conversive measures. No medical treatment is needed, advice on complete voice rest, humidified air inhaling, cessation of smoking, and dietary modification such as caffeine avoidance.
What is the Prognosis of Laryngitis?
The prognosis of laryngitis is good as it is self-limited and with conservative measures mortality is rare.