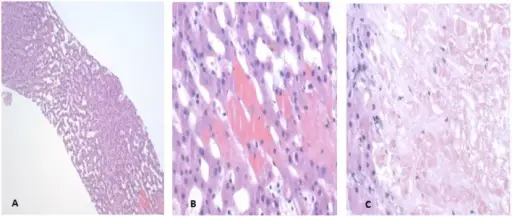
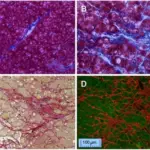
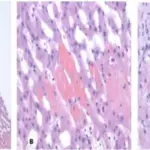
Left-sided heart failure is a heart condition where the left ventricle is weakened, resulting in inadequate pumping of oxygen-rich blood to the body. It has two types: systolic failure with reduced ejection fraction and diastolic heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.
What is the Pathology of Left-Sided Heart Failure?
Left sided heart failure pathology is due to gradual weakening of the left ventricle.
How does Left-Sided Heart Failure Present?
Left sided heart failure presents as shortness of breath, difficulty breathing when lying down, and swelling of the lower extremities. Features generally resemble general features of heart failure.
How does Left-Sided Heart Failure Present?
Diagnosis of left sided heart failure is based on cardiac catheterization, chest x-ray, electrocardiogram, 2D echo, and treadmill stress test. Radionuclide imaging can also be used to assess extent of heart damage.
How does Left-Sided Heart Failure Present?
Treatment of left sided heart failure consists of pharmacologic approaches such as use of diuretics, ACE inhibitors, and beta blockers. Lifestyle changes and surgery that may include a left ventricular assist device (LVAD) surgery, pacemaker, repair surgery, and coronary artery bypass graft (CABG).
What is the Prognosis of Left-Sided Heart Failure?
Left sided heart failure prognosis is poor with a mortality of 25% 1 year after diagnosis, and patients with an ejection fraction of <15% have mortality of 50% in less than one year.