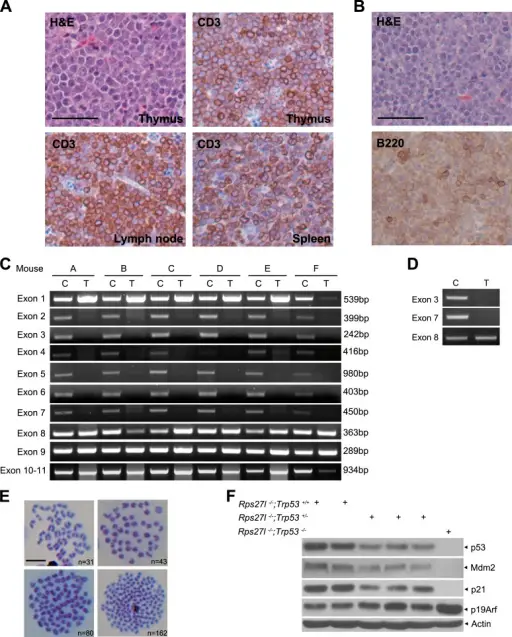
Li-Fraumeni syndrome is an inherited familial predisposition to a wide range of certain, often rare, cancers. This is due to a change (mutation) in a tumor suppressor gene known as TP53. The resulting p53 protein produced by the gene is damaged and is unable to help prevent malignant tumors from developing.
What is the Pathology of Li-Fraumeni Syndrome?
Etiology: The cause of Li-Fraumeni syndrome is mutation of the TP53 tumor suppressor gene on chromosome 17. LFS follows autosomal dominant inheritance.
Genes involved: TP53 tumor suppressor gene on chromosome 17.
Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to Li-Fraumeni syndrome is germline TP53 gene mutation.
Histology: The histology associated with Li-Fraumeni syndrome is nonspecific.
How does Li-Fraumeni Syndrome Present?
Patients with Li-Fraumeni syndrome typically are females and usually present at the age of 40 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with Li-Fraumeni syndrome include multiple cancers such as soft tissue sarcomas, osteosarcomas, leukemia, and gonadal tumors.
How is Li-Fraumeni Syndrome Diagnosed?
Li-Fraumeni syndrome is diagnosed based on the presence of a so called pathogenic or likely pathogenic variant in the TP53 gene.
How is Li-Fraumeni Syndrome Treated?
There is no standard treatment or cure for LFS or a germline TP53 gene variant. continues on how to best manage those cancers involved in LFS. This includes surgery, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy.
What is the Prognosis of Li-Fraumeni syndrome?
The prognosis of Li-Fraumeni syndrome poor.