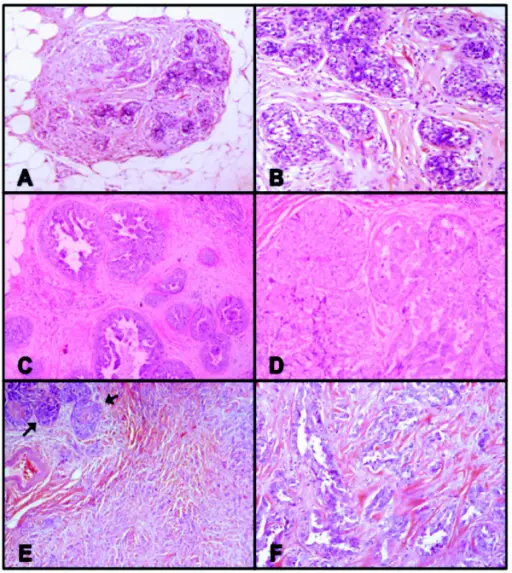
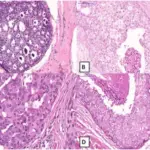
Lobular Carcinoma in Situ is the lobulocentric proliferation of small uniform cells which fill and distend most of the acini in the involved lobule.
What is the Pathology of Lobular Carcinoma in Situ?
The pathology of lobular carcinoma in situ is:
-Etiology: The cause of lobular carcinoma in situ are the genetic mutations developed in a milk-producing gland of a breast.
-Genes involved: Mutations in the CDH1.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to lobular carcinoma in situ is when genetic mutations occur in the DNA of breast duct cells.
-Morphology: The morphology associated with lobular carcinoma in situ may include breast assymetry or a mass lesion.
-Histology: The histology associated with lobular carcinoma in situ shows terminal duct lobular unit with expanding acini and proliferation loosley cohesive of monomorphic cells.
How does Lobular Carcinoma in Situ Present?
Patients with lobular carcinoma in situ typically are older females.
How is Lobular Carcinoma in Situ Diagnosed?
Lobular carcinoma in situ is diagnosed by biopsy and histologic examination.
How is Lobular Carcinoma in Situ Treated?
Lobular carcinoma in situ is treated with lumpectomy or mastectomy, and possible sentinel lymph node biopsy.
What is the Prognosis of Lobular Carcinoma in Situ?
The prognosis of lobular carcinoma in situ is fair.