Lupus nephritis is an autoimmune disease that affects the kidney.
What is the Pathology of Lupus Nephritis?
The pathology of lupus nephritis is:
-Etiology: The cause of lupus nephritis is genetic factors, immunologic factors, environmental factors.
-Genes involved: MBL2, TNF, CTLA4 genes.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to lupus nephritis is due to the autoimmune e disease that leads to the formation of antibodies and immune complexes which leads to renal damage and finally nephritis.
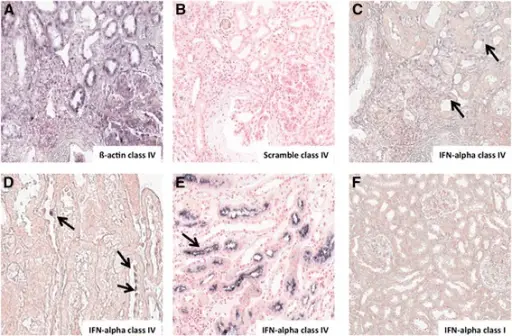
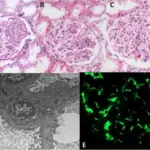
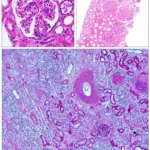
-Morphology: The morphology associated with lupus nephritis shows thickening of capillary walls.
-Histology: The histology associated with lupus nephritis shows mesangial or capillary immune deposits, increased mesangial cellularity, thickening of capillary walls,
How does Lupus Nephritis Present?
Patients with lupus nephritis typically are female present at the age range of 20-40 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with lupus nephritis are at first asymptomatic later fatigue, malar rash, discoid lupus, oral ulcers,photosensitivity hypoalbuminemia, joint pain, hematuria, proteinuria, serositis.
How is Lupus Nephritis Diagnosed?
Lupus nephritis is diagnosed through blood tests, urinalysis, ultrasound of the kidney, kidney biopsy, X-ray.
How is Lupus Nephritis Treated?
Lupus nephritis is treated with corticosteroids, cytotoxic agents, plasma exchange, rituximab.
What is the Prognosis of Lupus Nephritis?
The prognosis of lupus nephritis is fair with a survival rate of 73%.