Malignant mixed tumor is a rare tumor of salivary glands.
What is the Pathology of Malignant Mixed Tumor?
The pathology of malignant mixed tumor is:
-Etiology: The cause of malignant mixed tumor is from a pre-existing benign mixed tumor that mutates.
-Genes involved: PLAG1, HMGA2, MDM2, HER2, HMGIC, and TP53.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to malignant mixed tumor is malignant transformation of glandular cells.
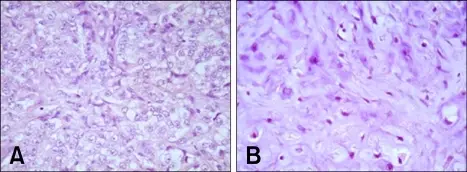
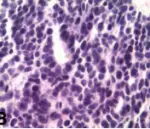
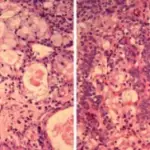
-Histology: The histology associated with malignant mixed tumor shows a carcinomatous component that may be salivary duct carcinoma, and a myoepithelial carcinoma or epithelial myoepithelial carcinoma.
How does Malignant Mixed Tumor Present?
Patients with malignant mixed tumor typically are older males. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with malignant mixed tumor include a palpable mass in the salivary gland.
How is Malignant Mixed Tumor Diagnosed?
Malignant mixed tumor is diagnosed by physical exam, fine needle aspiration, and biopsy.
How is Malignant Mixed Tumor Treated?
Malignant mixed tumor is treated by surgical excision.
What is the Prognosis of Malignant Mixed Tumor?
The prognosis of malignant mixed tumor is poor, with a 15% 5 year survival rate.