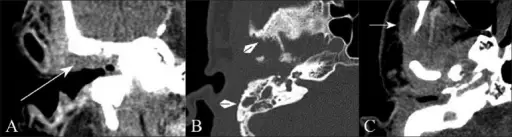
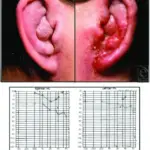
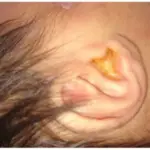
Malignant otitis externa is a potentially fatal external otitis due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
What is the Pathology of Malignant Otitis Externa?
The pathology of malignant otitis externa is:
-Etiology: The cause of malignant otitis externa Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to malignant otitis externa is an infection that affects the external ear.
-Histology: The histology associated with malignant otitis externa shows ulcerated or necrotic epithelium with pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia. A mixed inflammatory infiltrate may be present.
How does Malignant Otitis Externa Present?
Patients with malignant otitis externa typically are female present at the age range of older adults. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with malignant otitis externa include pain and headache, more severe than clinical signs would suggest, and foul-smelling greenish-yellow drainage from the ear.
How is Malignant Otitis Externa Diagnosed?
Malignant otitis externa is diagnosed with a physical exam. Ear drainage may be obtained and sent for microbial analysis.
How is Malignant Otitis Externa Treated?
Malignant otitis externa is treated with surgical debridement and antibiotics. Hyperbaric oxygen may also be used.
What is the Prognosis of Malignant Otitis Externa?
The prognosis of malignant otitis externa is poor.