Medullary carcinoma is a neuroendocrine tumor derived from C cells of the ultimobranchial body of the neural crest, which secrete calcitonin.
What is the Pathology of Medullary Carcinoma?
The pathology of medullary carcinoma is:
-Etiology: The cause of medullary carcinoma is unknown. Medullary carcinoma is associated with MEN 2A syndrome.
-Genes involved: RET.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to medullary carcinoma involves the gain of function mutations in the RET proto-oncogene, a 21-exon gene located on chromosome 10q11.
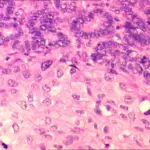
-Histology: The histology associated with medullary carcinoma shows islands of tumor cells having irregular borders, and amyloid.
How does Medullary Carcinoma Present?
Patients with medullary carcinoma typically present in either male or female present at the age range of 35-45. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with medullary carcinoma include hoarseness, dysphagia, respiratory difficulty, lump presence in the neck, and diarrhea.
How is Medullary Carcinoma Diagnosed?
Medullary carcinoma is diagnosed using fine-needle aspiration biopsy.
How is Medullary Carcinoma Treated?
Medullary carcinoma is treated with total thyroidectomy with cervical lymphadenectomy.
What is the Prognosis of Medullary Carcinoma?
The prognosis of medullary carcinoma is good with a 5-year survival rate.