Menetrier disease is the ridges along the inside of the stomach wall called rugae to enlarge, forming giant folds in the stomach lining. The rugae enlarge because of an overgrowth of mucous cells in the stomach wall. In a normal stomach, mucous cells in the rugae release protein-containing mucus.
What is the Pathology of Menetrier Disease?
The pathology of menetrier disease is:
-Etiology: The cause of menetrier disease is unknown.
-Genes involved: SMAD4.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to menetrier disease is incompletely understood but may involve transforming growth factor-alpha TGF-α. TGF-α increases gastric mucus production and inhibits acid secretion,241 and levels are usually elevated in the gastric mucous cells in patients with Ménétrier disease.
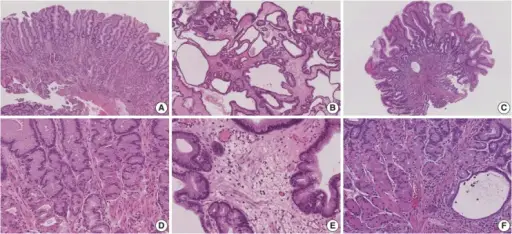
-Histology: The histology associated with menetrier disease shows evident by marked enlargement of gastric folds and rugae. On histopathological examination, foveolar hyperplasia, oxyntic glands atrophy, reduction in parietal acid-producing cells and chief pepsinogen- producing cells, and cystic dilation of pits are seen. The overall linear architecture is usually maintained. Edema and hyperplasia of smooth muscle in the lamina propria are observed.
How does Menetrier Disease Present?
Patients with menetrier disease typically more in male at age range 30-60 years mostly but cases in childhood are also reported. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with menetrier disease include: nausea and frequent vomiting, Diarrhea,loss of appetite, extreme weight loss, Malnutrition, low levels of protein in the blood.
How is Menetrier Disease Diagnosed?
Menetrier disease is diagnosed by computerized tomography CT scan, and biopsy.
How is Menetrier Disease Treated?
Menetrier disease is treated by anticholergic drugs, acid suppression therapy, and antibiotic therapy directed against H. pylori infection.
What is the Prognosis of Menetrier Disease?
The prognosis of menetrier disease is good. The prognosis of Ménétrier disease varies from person to person. Resolution of symptoms may occur in adults with an underlying Helicobacter Pylori H. Pylori infection once treatment of the infection occurs. Cases in children may resolve spontaneously or with treatment of the underlying CMV infection.