Mercury is a highly toxic heavy metal. Mercury toxicity is a type of metal poisoning due to exposure to mercury. Mercury may cause disease by inhalation of mercury vapors.
What is the Pathology of Mercury Toxicity?
The pathology of mercury toxicity is:
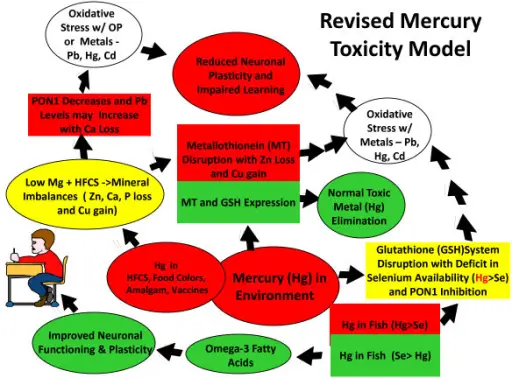
-Etiology: The cause of mercury toxicity is that it binds sulfhydryl groups in proteins. Mercury causes damage to the kidneys and central nervous system.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to mercury toxicity includes binding of mercury to sulfhydryl groups and incapacitating key enzymes involved in the cellular stress response, protein repair, and oxidative damage prevention.
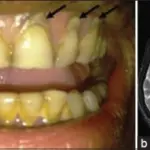
-Morphology: The morphology associated with mercury toxicity shows that a certain mercury compound, dimethylmercury, is so toxic that even a few microliters spilled on the skin, or even on a latex glove, can cause death.
-Histology: The histology associated with mercury toxicity shows axonal and demyelinating changes.
How does Mercury Toxicity Present?
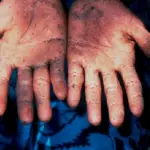
Patients with mercury toxicity are typically females. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with mercury toxicity include muscle weakness, poor coordination, numbness in the hands and feet, skin rashes, anxiety, memory problems, trouble speaking, trouble hearing, or trouble seeing.
How is Mercury Toxicity Diagnosed?
Mercury toxicity is diagnosed by determining the history of exposure, physical findings, and an elevated body burden of mercury.
How is Mercury Toxicity Treated?
Mercury toxicity is treated with chelation therapy.
What is the Prognosis of Mercury Toxicity?
The prognosis of mercury toxicity is good with reversible changes, however, prolonged exposure can do irreversible damage.