Metabolic liver disease disorder in which abnormal chemical reactions in the body disrupt metabolism
What is the Pathology of Metabolic Liver Disease?
The pathology of metabolic liver disease is:
-Etiology: The cause of the metabolic liver disease is genetic.
-Genes involved: PiZZ.
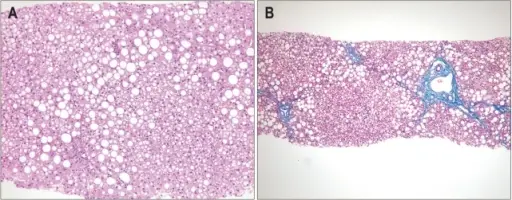
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to metabolic liver disease shows necrosis of hepatocytes stimulates immune cells to release cytokines, growth factors, and various unknown chemicals.
-Histology: The histology associated with metabolic liver disease shows hepatocellular rosette formation.
How does Metabolic Liver Disease Present?
Patients with metabolic liver disease typically affect males present at the age range of 35-55. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with metabolic liver disease include itching, jaundice, difficulty gaining weight, low blood sugar level, fat-soluble vitamin deficiencies, liver scarring, and fatigue.
How is Metabolic Liver Disease Diagnosed?
Metabolic liver disease is diagnosed using a blood test and urine analysis.
How is Metabolic Liver Disease Treated?
Metabolic liver disease is treated using therapeutic phlebotomy.
What is the Prognosis of Metabolic Liver Disease?
The prognosis of metabolic liver disease is fair with a life expectancy of up to 10 years.