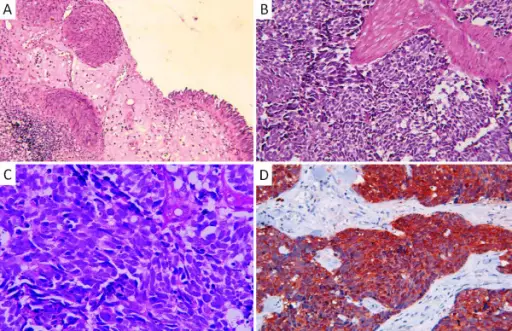
Mixed carcinoma of the bladder is mixed high- and low-grade carcinoma of the bladder.
What is the Pathology of Mixed Carcinoma?
The pathology of mixed carcinoma is:
-Etiology: The etiology of mixed carcinoma is environmental exposure.
-Genes involved: FGFR-3, Ras, PIK3CA, PTEN.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to Mixed carcinoma is the molecular pathways that are likely responsible for the development of noninvasive and invasive bladder tumors.
-Morphology: The morphology associated with mixed carcinoma shows variable features.
-Histology: The histology associated with mixed carcinoma shows features of both high grade and low-grade tumors.
How does Mixed Carcinoma Present?
Patients with mixed carcinoma typically affect males. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with mixed carcinoma include painless gross hematuria.
How is Mixed Carcinoma Diagnosed?
Mixed carcinoma is diagnosed by cytology, imaging, and biopsy.
How is Mixed Carcinoma Treated?
Mixed carcinoma is treated by surgical resection.
What is the Prognosis of Mixed Carcinoma?
The prognosis of mixed carcinoma is variable.