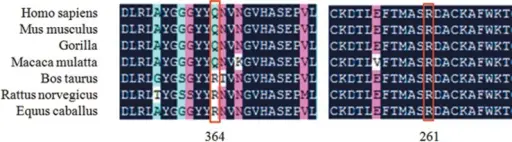
Molecular genetic diagnosis is a collection of techniques used to analyze biological markers in the genome and proteome, and how their cells express their genes as proteins, applying molecular biology to medical testing.
What are Diagnostic Methods and Indications for Genetic Testing?
Diagnostic Methods:
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
- DNA Sequencing (Sanger sequencing, next-generation sequencing)
- Cytogenetics (Karyotyping and FISH); microarray testing
- Gene expression profiling
Indications for genetic tests are typically for conformational diagnosis, or to determine genetic risk.
What is Polymerase Chain Reaction Testing?
Polymerase chain reaction testing is a method widely used to rapidly make millions to billions of copies of a specific DNA sample to see what genes are present.
What is Molecular Analysis of Genomic Alterations?
Molecular analysis of genomic alterations is used to profile gene expression levels of thousands of genes at the same time to study certain diseases and treatments. This is able to detect single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and copy number variations (CNVs) for a variety of applications including genotyping, clinical genetic testing, forensic analysis, cancer mutations, and genetic linkage analysis.
Examples of molecular analysis of genomic alterations include:
- Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH)
- Multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA)
- Southern blotting
- Cytogenomic array technology
What is Fluorescence in Situ Hybridization (FISH)?
Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) is a laboratory technique for detecting and locating a specific DNA sequence on a chromosome. FISH relies on exposing chromosomes to a small DNA sequence (a probe) with an attached fluorescent molecule attached to it. The probe sequence binds to its corresponding sequence on the chromosome.
What is Multiplex Ligation-Dependent Probe Amplification (MLPA)?
Multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA) is a variation of the multiplex polymerase chain reaction that permits amplification of multiple targets with only a single primer pair. Multiplex ligation dependent probe amplification detects copy number changes at the molecular level. Specialized software programs are used for analysis. Identification of duplications or deletions may indicate pathogenic mutations.
What is Southern Blotting?
Southern blotting is a laboratory technique used to detect specific DNA molecules. Southern blots can be used to analyze an organism’s total DNA, also known as its genome, in order to identify a specific sequence of interest.
What is Cytogenomic Array Technology?
Cytogenomic array technology is microarray-based technologies for the investigation of specific loci and the entire genome.
What are Polymorphic Markers?
Polymorphic markers are a gene or DNA sequence with a known location on a chromosome that can be used to identify individuals or species.
What is Molecular Diagnosis?
Molecular diagnosis is a collection of techniques that are used to analyze genetics of biological specimens.
What is Genome-Wide analysis?
Genome-wide analysis is a genetic test that can scan the entire genome to find specific genetic patterns.
What are Epigenetic Alterations?
Epigenetic alterations are environmentally induced changes in the chemical structure or expression of DNA that does not change the DNA coding sequence. Epigenetic alterations may occur when methyl groups are added to or removed from DNA, or when changes are made to histones. These changes may occur with age and exposure to environmental factors, such as exercise, change in diet, and exposure to sunlight.
What is RNA Analysis?
RNA analysis is a multistage process that includes cloning, physical mapping, subcloning, sequencing, and information analysis of an RNA sequence.
What is Bioinformatics?
Bioinformatics is a subdiscipline of biology and computer science focused on analysis, acquisition, storage, and dissemination of biological information, especially DNA and proteomics.
What is Next Generation Sequencing?
Next generation sequencing is technology that allows rapid study of genomics and molecular biology.