Mucoepidermoid carcinoma is a malignant glandular neoplasm of the salivary glands.
What is the Pathology of Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma?
The pathology of mucoepidermoid carcinoma is:
-Etiology: The cause of mucoepidermoid carcinoma thought o be due to environmental or genetic factors.
-Genes involved: MAML2 fusion.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to mucoepidermoid carcinoma is malignant stem or progenitor cells in excretory ducts.
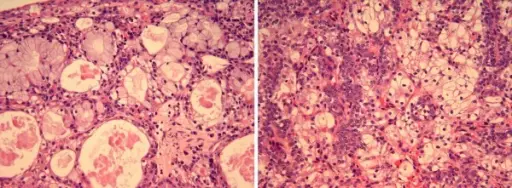
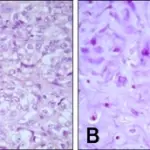
-Histology: The histology associated with mucoepidermoid carcinoma shows solid, cystic or mixed growth patterns that may have papillary or glandular growth patterns.
How does Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma Present?
Patients with mucoepidermoid carcinoma typically are females that are older. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with mucoepidermoid carcinoma include a painless swelling mass that might cause slight pressure.
How is Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma Diagnosed?
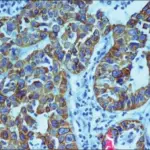
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma is diagnosed by physical exam, fine needle aspiration, and biopsy.
How is Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma Treated?
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma is treated by complete surgical resection.
What is the Prognosis of Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma?
The prognosis of mucoepidermoid carcinoma is poor.