Mucormycosis is an opportunistic contagion caused by mold fungi, that including Rhizopus, Absidia, Mucorall, Cunninghamella, and belong to the class Zygomycetes.
What is the Pathology of is Mucormycosis?
The pathology of is mucormycosis is:
-Etiology: The cause of mucormycosis is Fungal bread mold fungi. Other predisposing factors; neutropenia, corticosteroid use, diabetes mellitus, and breakdown of the cutaneous barrier.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to mucormycosis. Fungal is transmitted through airborne asexual spores. Inhaled or through percutaneous, causes infection to the sinus and or lungs. There is phagocytic and oxidative elimination of spore largely by macrophage cells (neutrophils) throughout established infection.
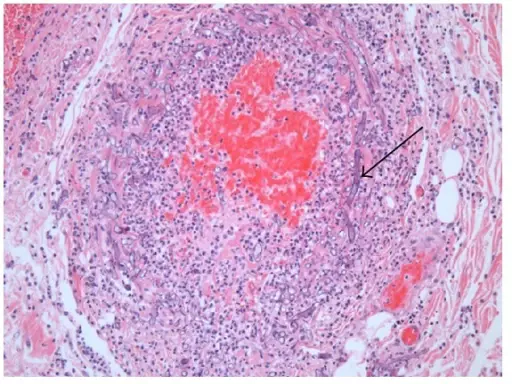
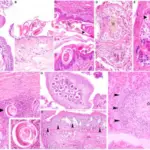
-Histology: The histology associated with mucormycosis shows pathognomonic broad, asymmetrical, ribbonlike, hyphae with uneven branching. Neutrophil infiltration, tissue infarction, and vessel invasion are observed. A granulomatous reaction was also seen.
How does Mucormycosis Present?
Patients with mucormycosis typically since is not a notifiable illness, the true prevalence is mysterious. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with mucormycosis include: facial pain, nasal congestion, numbness, black discharge retro-orbital headache, dyspnea, fever, hemoptysis, abdominal pain, and cellulitis.
How is Mucormycosis Diagnosed?
Mucormycosisis diagnosed through laboratory tests: Complete blood cell (CBC) count for neutropenia. Arterial blood gas (ABG) study assesses for acidosis. Blood cultures to check for bacteremia. Molecular based testing using fresh tissue over paraffin tissue. Biopsy for histology. Radiologic Studies; CT scan of the sinuses, brain, chest, and abdomen. Sinuses and brain Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
How is Mucormycosis Treated?
Mucormycosis is treated as follows. Medical care; Treating the underlying abnormality, managing DKC, and correcting neutropenia. Prompt antifungal therapy first-line liposomal amphotericin B. Surgical interventions, necrotic tissue debridement. Drainage of the sinuses and excision of the orbital contents and affected brain tissue.
What is the Prognosis Mucormycosis?
The prognosis of Mucormycosisis poor. Mortality due to mucormycosis fluctuates flanked by 40%-80%, despite treatment advancements.