Mucormycosis fungal Infection is previously called zygomycosis, a serious but rare fungal infection caused by a group of molds called mucormycetes.
What is the Pathology of Mucormycosis Fungal Infection?
The pathology of mucormycosis fungal infection is:
-Etiology: The cause of mucormycosis fungal infection is a group of molds called mucormycetes.
-Genes involved: Not applicable.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to mucormycosis fungal infection are:
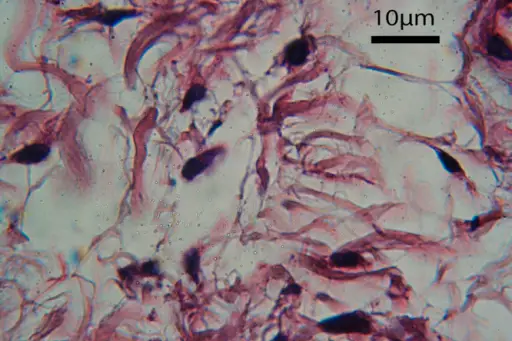
-Morphology: The morphology associated with mucormycosis fungal infection shows large, ribbon-like hyphae with irregular diameter and only occasional septae, hence, their frequent characterization in tissue as aseptate fungi.
-Histology: The histology associated with mucormycosis fungal infection shows broad pauciseptate ribbon-like hyphae with irregular branching at 90° angles.
How does Mucormycosis Fungal Infection Present?
Patients with mucormycosis fungal infection typically are all genders of all ages. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with mucormycosis fungal infection include nasal or sinus congestion, black lesions on the nasal bridge, fever, and headache.
How is Mucormycosis Fungal Infection Diagnosed?
Mucormycosis fungal infection is diagnosed by laboratory tests or tissue samples.
How is Mucormycosis Fungal Infection Treated?
Mucormycosis fungal infection is treated by antifungal medicine amphotericin B, posaconazole, or isavuconazole.
What is the Prognosis of Mucormycosis Fungal Infection?
The prognosis of mucormycosis fungal infection is poor.