Muir-Torre syndrome is a form of lynch syndrome characterized by oil gland skin tumors mostly affecting the gastrointestinal tract.
What is the Pathology of Muir-Torre?
The pathology of muir-torre syndrome is the scientific study of the oil gland tumors in the gastrointestinal tract.
-Etiology: The cause of muir-torre syndrome is gene mutation.
-Genes involved: MS2, MLH1, MLH6 and the MLH3 genes.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to Muir-Torre syndrome is genetic.
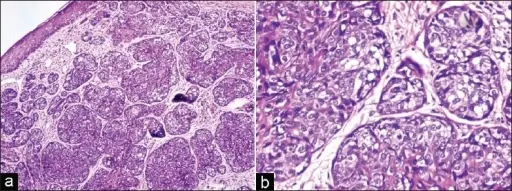
-Morphology: The morphology associated with muir-torre syndrome shows unevenly sized, partly differentiated sebaceous lobules.
-Histology: The histology associated with muir-torre syndrome shows a sebaceous cell with prominent cytoplasmic vacuoles.
How does Muir-Torre Syndrome Present?
Patients with muir-torre syndrome typically males are more affected than the female with the age ranging from the young adults to the elderly. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with muir-torre syndrome include the presence of a sebaceous tumor, internal malignancy, familial history of cancer mostly the close relatives.
How is Muir-Torre Syndrome Diagnosed?
The Muir-Torre syndrome is diagnosed physical examination, history taking, dermatoscopy, confocal microscopy.
How is Muir-Torre Syndrome Treated?
The Muir-Torre syndrome is treated by oral isotretinoin and surgical removal.
What is the Prognosis of Muir-Torre Syndrome?
The prognosis of muir-torre syndrome is poor due to the high rate of recurrence even after surgical removal.