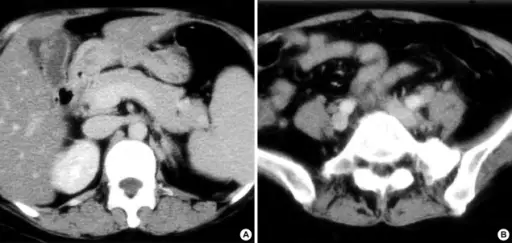
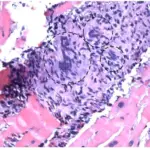
Multiple organ dysfunction (MOD) is the development of potentially reversible physiologic damage to two or more organ systems.
What is the Pathology of Multiple Organ Dysfunction?
The pathology of multiple organ dysfunction is:
-Etiology: The cause of multiple organ dysfunction is typically infection, hypoperfusion, or organ trauma.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to multiple organ dysfunction typically includes sepsis or systemic inflammatory response syndrome.
How does Multiple Organ Dysfunction Present?
Patients with multiple organ dysfunction typically affect males and females present at the age range of 40 and above. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with multiple organ dysfunction include an altered mental state, decrease in renal perfusion, and respiratory issues.
How is Multiple Organ Dysfunction Diagnosed?
Multiple organ dysfunction is diagnosed clinically.
How is Multiple Organ Dysfunction Treated?
Multiple organ dysfunction is treated with organ transplant and supportive care.
What is the Prognosis of Multiple Organ Dysfunction?
The prognosis of multiple organ dysfunction is poor.