Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disorder that leads to blockade at the neuromuscular junction causing antibodies to form against acetylcholine receptors causing muscle weakness.
What is the Pathology of Myasthenia Gravis?
The pathology of myasthenia gravis is:
-Etiology: The cause of myasthenia gravis is idiopathic but may be induced by drugs,
-Genes involved: NA.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to myasthenia gravis antibodies inhibit acetylcholine binding leading to muscle weakness.
-Morphology: NA.
-Histology: NA.
How does Myasthenia Gravis Present?
Patients with myasthenia gravis, typically female, are more present at the age range of 28 years in females and 42 years in males. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with myasthenia gravis include painless specific muscle weakness, droopy eyelids, double vision, slurred speech, difficulty in swallowing, sad-looking facial appearance.
How is Myasthenia Gravis Diagnosed?
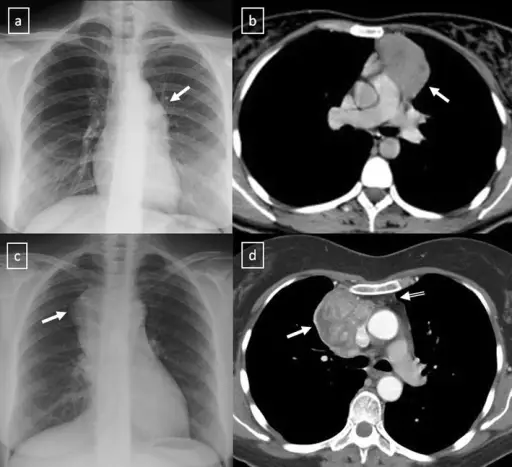
Myasthenia gravis is diagnosed with a history and physical exam, antibody testing, rheumatoid factor testing, radiography, CT scan, MRI.
How is Myasthenia Gravis Treated?
Myasthenia gravis is treated by a combination of cholinesterase inhibitors, immunosuppressors, plasmapheresis, immunotherapy, and supportive care.
What is the Prognosis of Myasthenia Gravis?
The prognosis of myasthenia gravis is good since the drugs used to reduce the mortality rate to 2-3%