Neck pathology is the study of diseases and disorders that effect the neck.
Examples of pathologic conditions involving the neck include:
- Brachial cysts
- Thyroglossal duct cysts
- Paragangiomas
What are Brachial Cysts?
Brachial cysts are due to a failure of obliteration of the second branchial cleft during embryologic development. Bracial cleft cysts are also known as or cervical lymphoepithelial cysts. Brachial cysts are congenital disorders that form during the fourth week of gestation.
What is the Pathology of Brachial Cysts?
The pathology of branchial cysts is:
-Etiology: The cause of branchial cyst is incomplete involution of branchial cleft structures.
-Genes involved: Unknown.
-Pathogenesis: The internal opening of the branchial sinuses arising from incomplete obliteration in embryogenesis.
-Morphology: They may be on the anterior neck and upper chest bumps.
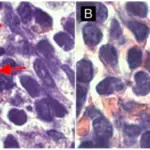
-Histology: The histology associated with branchial cysts shows cysts lined by stratified squamous epithelium that may contain keratinous debris.
How do Branchial Cysts Present?
Patients with branchial cyst typically are equally common in males and females and usually present in childhood or early adulthood. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with branchial cyst include neck lumps.
How are Branchial Cysts Diagnosed?
Branchial cysts are diagnosed by ultrasound and biopsy.
How are Branchial Cysts Treated?
Branchial cyst is treated by surgical resection.
What is the Prognosis of Branchial Cysts?
The prognosis of branchial cyst is good.
What are Thyroglossal Duct Cysts?
Thyroglossal duct cysts are fluid filled cysts in the front part of neck.
What is the Pathology of Thyroglossal Duct Cysts?
The pathology of thyroglossal duct cysts is:
-Etiology: The cause of thyroglossal duct cysts is result of obliteration of the thyroglossal duct.
-Genes involved: Unknown.
-Pathogenesis: Failure of the thyroglossal duct to obliterate.
-Histology: The histology associated with thyroglossal duct cysts shows as cystic structures lined by respiratory epithelium, squamous epithelium, or a combination of both.
How does Thyroglossal Duct Cysts Present?
Patients with thyroglossal duct cysts typically are children with a neck mass.
How are Thyroglossal Duct Cysts Diagnosed?
Thyroglossal duct cysts is diagnosed by ultrasound.
How are Thyroglossal Duct Cysts Treated?
Thyroglossal duct cysts is treated by surgical resection, particularly the Sistrunk operation.
What is the Prognosis of Thyroglossal Duct Cysts?
The prognosis of thyroglossal duct cysts is great.
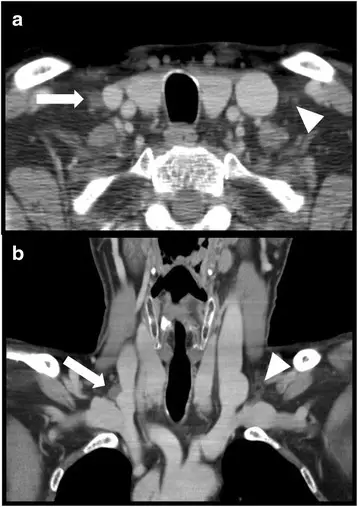
What are Paragangliomas?
Paragangliomas are neoplasms that originate from nervous system.
What is the Pathology of Paragangliomas?
The pathology of paraganglioma is:
-Etiology: The cause of paragangliomas are neuroendocrine neoplasms, derived from paraganglia of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems.
-Genes involved: MEN 2A, MEN 2B, RET, VHL, NF1
-Pathogenesis: Proliferation of neuroendocrine cells.
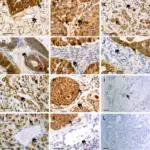
-Histology: The histology associated with paraganglioma shows usually composed of solid nests of round to oval or elongated cells with abundant granular cytoplasm without mitosis or necrosis.
How do Paragangliomas Present?
Patients with paraganglioma are more prevalent in middle-aged females and typically present as slowly growing mass.
How are Paragangliomas Diagnosed?
Paraganglioma is diagnosed via diagnostic tests imaging scans and biopsy.
How are Paragangliomas Treated?
Paragangliomas are treated by surgical excision.
What is the Prognosis of Paragangliomas?
The prognosis of paragangliomas is good.