Nephrogenic adenoma of the bladder is a benign polypoid, papillary, fungiating, or velvety lesion found in the bladder or prostatic urethra after urothelial injury which has multiple histologic patterns.
What is the Pathology of Nephrogenic Adenoma of the Bladder?
The pathology of nephrogenic adenoma of the bladder is:
-Etiology: The cause of nephrogenic adenoma of the bladder is urinary tract infections.
-Genes involved: PAX2, PAX8, AMACR, CD10, CK7, GATA3, CK903.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to a nephrogenic adenoma is the metaplastic lesion.
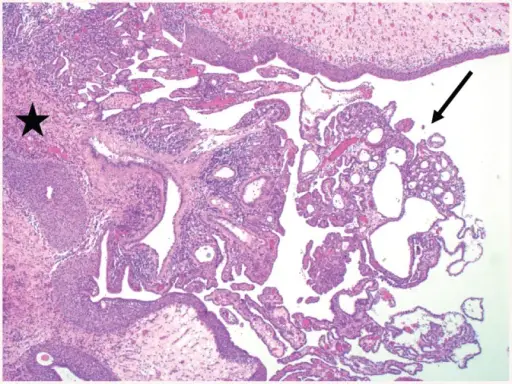
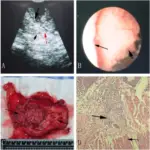
-Morphology: The morphology associated with nephrogenic adenoma of the bladder shows friable soft tissue fragments.
-Histology: The histology associated with nephrogenic adenoma of the bladder shows tubules lined by cuboidal or hobnail cells.
How is Nephrogenic Adenoma of the Bladder Diagnosed?
Nephrogenic adenoma of the bladder is diagnosed by biopsy.
How is Nephrogenic Adenoma of the Bladder Treated?
Nephrogenic adenoma of the bladder is treated with urinary bladder is resection and antibiotics.
What is the Prognosis of Nephrogenic Adenoma of the Bladder?
The prognosis of nephrogenic adenoma of the bladder is variable.