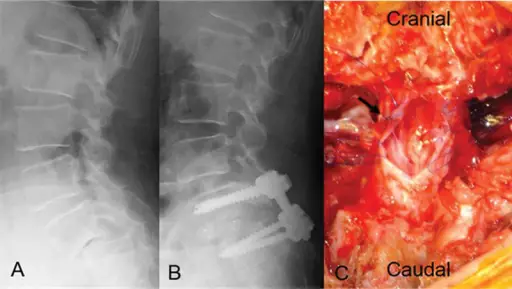
Neurogenic shock results from loss of vascular tone associated with anesthesia or secondary to a spinal cord injury.
What is the Pathology of Neurogenic Shock?
The pathology of neurogenic shock is:
-Etiology: The cause of neurogenic shock is autonomic dysregulation following spinal cord injury, usually as a result of to trauma.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to neurogenic shock includes the injury to the spinal cord above the level of T6 which results in hemodynamic changes.
How does Neurogenic Shock Present?
Patients with neurogenic shock are typically males or females 15 years of age or older. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with neurogenic shock include low heart beats, hypotension, and temperature dysregulation.
How is Neurogenic Shock Diagnosed?
Neurogenic shock is diagnosed via CT scan, MRI, hemodynamic monitoring, and clinical exam.
How is Neurogenic Shock Treated?
Neurogenic shock is treated with hemodynamic stabilization, intravenous fluid resuscitation, vasopressors, and inotropes.
What is the Prognosis of Neurogenic Shock?
The prognosis of neurogenic shock is good if properly managed. The overall prognosis depends on the extent of spinal cord injury and response to treatment.