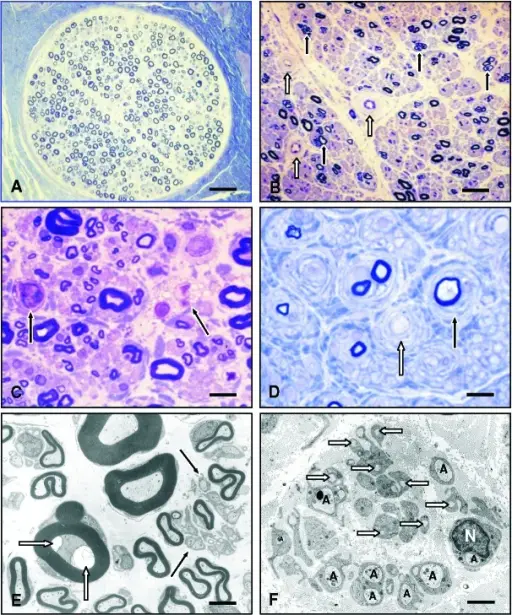
Neuropathy due to Inherited metabolic diseases is the disease of the nervous system caused by a chemical disruption in the body that leads to the alteration of the structure and the function of the myelin and the axons.
What is the Pathology of Neuropathy due to Inherited Metabolic Diseases?
The pathology of neuropathy due to inherited metabolic diseases is:
-Etiology: The cause of neuropathy due to inherited metabolic diseases is inherited disorders such as porphyria, uremia, and diabetes.
-Genes involved: NA.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to neuropathy due to inherited metabolic diseases is not well known but various factors can lead to it. They include diabetic polyneuropathy.
-Morphology: NA.
-Histology: NA.
How does Neuropathy due to Inherited Metabolic Diseases Present?
Patients with neuropathy due to inherited metabolic disorders typically are males and females present at the age range of 60-70 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with neuropathy due to inherited metabolic diseases include numbness, difficulty in walking, lethargy, poor appetite,
How is Neuropathy due to Inherited Metabolic Diseases Diagnosed?
Neuropathy due to inherited metabolic diseases is diagnosed through history taking, physical examination, sensory and motor testing, urinalysis, thyroid function tests.
How is Neuropathy due to Inherited Metabolic Disorders Treated?
Neuropathy due to inherited metabolic diseases is treated and management of the underlying metabolic disorder is the main approach.
What is the Prognosis of Neuropathy due to Inherited Metabolic Diseases?
The prognosis of neuropathy due to inherited metabolic diseases is good depending on how well you will manage the underlying condition.