Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome is a pattern of multiple organ abnormalities caused by the mutation of the PTCH gene causing multiple basal cell skin cancer.
What is the Pathology of Nevoid Basal Cell Carcinoma?
The pathology of nevoid basal cell carcinoma is:
-Etiology: The cause of nevoid basal cell carcinoma is mostly mutation of genes, UV light exposure and radiation.
-Genes involved: PTCH1 and PTCH2 and the SUFU genes
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to nevoid basal cell carcinoma are genetic.
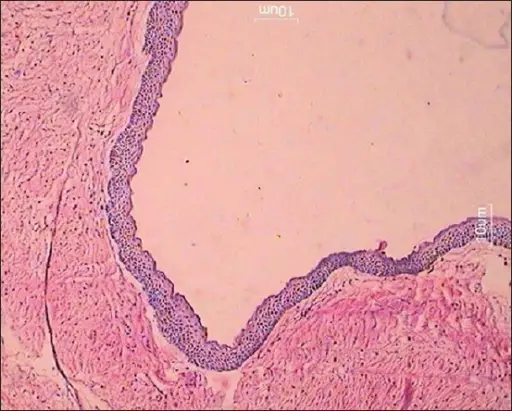
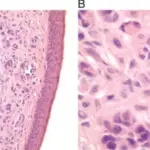
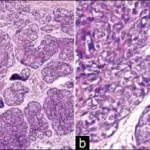
-Morphology: The morphology associated with nevoid basal cell carcinoma are skin lesions.
-Histology: The histology associated with nevoid basal cell carcinoma are melanocytic neoplasms.
How does Nevoid Basal Cell Carcinoma Present?
Patients with nevoid basal cell carcinoma typically may occur from the age of 20 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with nevoid basal cell carcinoma include cysts of the jaws, calcium deposition in the brain, pits on the palm of the hands and skeletal bone changes.
How is Nevoid Basal Cell Carcinoma Diagnosed?
The nevoid basal cell carcinoma is diagnosed by physical examination, CT scan and MRI.
How is Nevoid Basal Cell Carcinoma Treated?
The nevoid basal cell carcinoma is treated surgically and chemotherapy and also management of the symptoms.
What is the Prognosis of Nevoid Basal Cell Carcinoma?
The prognosis of nevoid basal cell carcinoma is fair.