Nodal marginal zone lymphoma is a primary lymph node disease with morphologic and immunophenotypic features similar to those of splenic marginal zone lymphoma and extranodal marginal zone lymphoma.
What is the Pathology of Nodal Marginal Zone Lymphoma?
The pathology of nodal marginal zone lymphomas is:
-Etiology: The cause of nodal marginal zone lymphomas is is not known. It is more common in people who have been infected with hepatitis C virus and some autoimmune conditions.
-Genes involved: Ig gene
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to nodal marginal zone lymphomas involve many oncogenic mutations of NOTCH, NF-κB, B-cell receptor and toll-like receptor signaling in mature B-cells differentiation into the marginal zone B-cells.
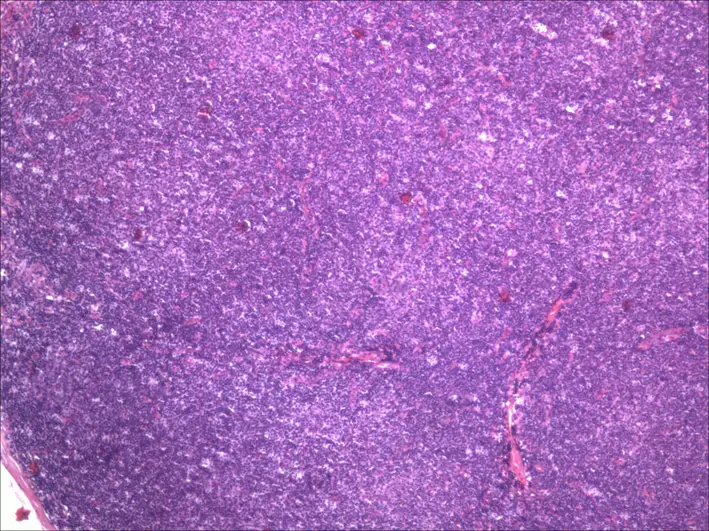
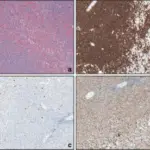
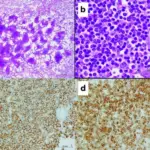
-Histology: The histology associated with nodal marginal zone lymphomas shows perifollicular and interfollicular lymphoid infiltrate that surrounds variably preserved germinal centers; diffuse pattern of infiltration can also be seen.
How does Nodal Marginal Zone Lymphoma Present?
Patients with nodal marginal zone lymphoma typically are women more than men and present at age range of 60 years or older. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with nodal marginal zone lymphomas include B symptoms, which are unexplained fever, drenching night sweats and unexplained weight loss, localized or generalized peripheral lymphadenopathy.
How is Nodal Marginal Zone Lymphoma Diagnosed?
Nodal marginal zone lymphoma is diagnosed by biopsy of affected lymph node.
How is Nodal Marginal Zone Lymphoma Treated?
Nodal marginal zone lymphoma is treated by watchful waiting, single chemotherapy (fludarabine or bendamustine), combination chemotherapy (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine and prednisone), targeted therapy (rituximab or ibritumomab), immunotherapy (interferon alpha) and radiation therapy.
What is the Prognosis of Nodal Marginal Zone Lymphoma?
The prognosis of nodal marginal zone lymphomas is less favorable than that of splenic marginal zone lymphoma and MALT lymphoma, with reported 5-year overall survival rates ranging between 55% and 89%.